Project Scope:
The I Kare Robo (IKROBO©) is a 3-year research project that includes the following technology divisions at Durham College – Electronics Engineering Technology, Bio-medical Engineering Technology, Mechatronics Engineering Technology and Mechanical Engineering Technology with the following aims:
1.To create a modern technology based wheelchair that will help improve the mobility of people with disabilities.
a. User can change the mode of mobility with a choice of 3 modes: Chair, bed and walker, with a push of a button.
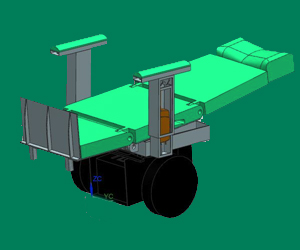
Bed Position

Walker Position
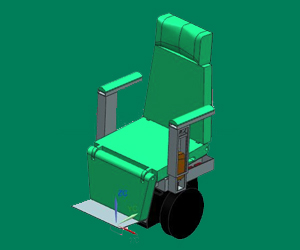
Chair Position
b. The chair can be controlled in chair and walker modes with four interfaces:
- Joystick (standard option)
- Voice activated interface
- Eye movement interface
- TouchPad interface
- Can be trained to memorize different routes with a closed environment
- Follows the predetermined path automatically by avoiding obstacles
- 911 alert with GPS interface for easy location (by 2016)
- Body temperature
- Heart rate
- Blood pressure
- Weight
- Blood glucose
- EEG/ EMG
- Surrounding air quality
- BMI (calculation)
- Lifting to and from bed from a wheel chair.
- Taking care for the patients’ daily activities.
c. Automatic Navigation Features:
2. To monitor health information for creating alerts and record keeping:
 a. Sensors to monitor Physiological signals of the user are built-in on wheelchair:
a. Sensors to monitor Physiological signals of the user are built-in on wheelchair:
b. Stores captured health data on the Internet cloud or on the internal storage for further analysis by the health care people.
c. Alerting nursing staff or other caregivers to patient hyperactivity, which may indicate that the patient is experiencing discomfort, but it also detects a lack of activity which may indicate illness or depression.
d. Medications schedules and appointment reminders (by 2016)
e. Assist healthcare personnel in safe handling of patients who are unable to move under their own power: (by 2016)
3. To provide Wheeltainment© (wheel entertainment) through built-in tablet:
a. Listen text using text to speech interface
b. Play video games
c. Watch movies and other Internet entertainment programs
d. Read news papers

